Check out the full series of Questions Management tutorial here.
To build the API adding a new category in the Core Category Service, there are a few things we need to do first:
The first thing we need to add an interface named CategoryRepository to manipulate with MongoDB server.
This interface will be in the com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.repository package, which extends from the ReactiveMongoRepository interface of Spring Data MongoDB Reactive.
The content of the CategoryRepository interface is as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
package com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.repository; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.ReactiveMongoRepository; import com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.document.Category; public interface CategoryRepository extends ReactiveMongoRepository<Category, String> { } |
with Category object:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
package com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.document; import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank; import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document; import lombok.Data; @Data @Document public class Category { @Id private String id; @NotBlank private String code; @NotBlank private String name; private String description; } |
You can see the tutorial Reactive REST APIs with Spring Data MongoDB Reactive and Spring WebFlux for more information.
Next we will configure the connection to the MongoDB server.
Currently, I am using MongoDB server without authentication mode, so I just declare the following in application.properties file:
|
1 |
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/qm |
I will run this service using port 8082 so I will add the server.port property in the application.properties file as follows:
|
1 |
server.port=8082 |
OK, everything is ready, now I will go to the main part of this tutorial.
I will create a controller named CategoryController with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
package com.huongdanjava.categoryservice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/category") public class CategoryController { } |
With this declaration, I expose APIs for the Core Category Service with the request URL starting with “/category”.
To work with the MongoDB server, we need to use the CategoryRepository interface, so I will declare it in the CategoryController class as follows:
|
1 2 |
@Autowired private CategoryRepository categoryRepository; |
To build the API adding a new category, I would add a new method to expose a POST request “/add” with data in the body as the Category object:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@PostMapping("/add") public Mono<Category> createCategory(@RequestBody Category category) { } |
Because Spring Data MongoDB Reactive has provided us the save() method to save the data to MongoDB, so I just need to call for using this method:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@PostMapping("/add") public Mono<Category> createCategory(@RequestBody Category category) { return categoryRepository.save(category); } |
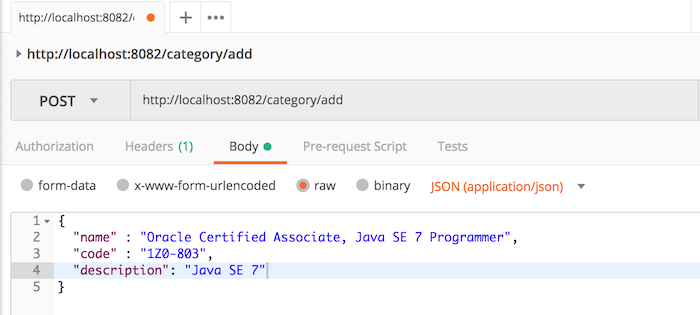
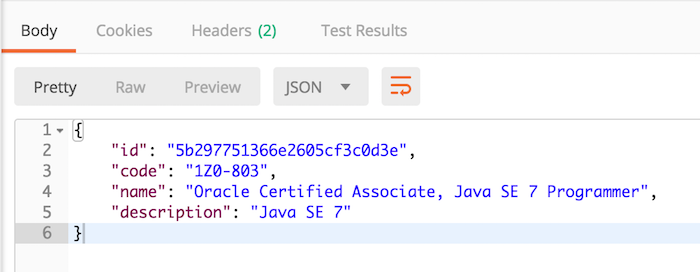
At this point, we have completed the construction for the API adding a new category for the Core Category Service, let’s try to test it.
Request:
Response:
The last thing we need to do is: add new Unit Test to the code we just added.
The Category object and CategoryRepository, nothing to test, right? What we need to test is the CategoryController.
I will create a class named CategoryControllerTest located in the src/test/java package to test the CategoryController class.
The principle of the Unit Test is that we will mock all the code invoked outside the method we need to test. Currently, in our CategoryController class there is only one method, and in this method, it is calling the save() method of the CategoryRepository class, so we will mock the CategoryRepository class.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
package com.huongdanjava.categoryservice; import org.mockito.Mock; import com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.repository.CategoryRepository; public class CategoryControllerTest { @Mock private CategoryRepository categoryRepository; } |
Check out more about Mockito’s @Mock annotation here.
Next, I will use @InjectMocks annotation to use the mock object of CategoryRepository in CategoryController as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
package com.huongdanjava.categoryservice; import org.mockito.InjectMocks; import org.mockito.Mock; import com.huongdanjava.categoryservice.repository.CategoryRepository; public class CategoryControllerTest { @Mock private CategoryRepository categoryRepository; @InjectMocks private CategoryController categoryController; } |
To use mock objects, we have to initialize them before testing a method, so I will add a method with the JUnit @Before annotation as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@Before public void init() { MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); } |
The code to test the createCategory() method is as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
@Test public void testCreateCategory() { // Create document need to insert into MongoDB Category category = new Category(); category.setCode("ABC"); category.setName("ZXC"); // The result should be the same with additional id field Category result = category; result.setId("123"); // Mock save() method of CategoryRepository when(categoryRepository.save(category)).thenReturn(Mono.just(result)); // Call method Mono<Category> createdCategoryAsMono = categoryController.createCategory(category); Category createdCategory = createdCategoryAsMono.block(); // Assertions assertEquals("ABC", createdCategory.getCode()); assertEquals("ZXC", createdCategory.getName()); assertEquals("123", createdCategory.getId()); } |
Running “Maven test” in the STS, you will not see any problem.


