MongoDB is one of the database systems that supports the Reactive mechanism through the use of its MongoDB Reactive Streams Java Driver. Together with Spring Data MongoDB, Spring also introduces us to the Spring Data MongoDB Reactive module which helps us minimize repetitive code when using the MongoDB Reactive Streams Java Driver. In this tutorial, through an example of building Reactive REST APIs, I show you how to use Spring Data MongoDB Reactive with Spring WebFlux.
First, I will create a Spring Boot project with Reactive MongoDB and Reactive Web as follows:
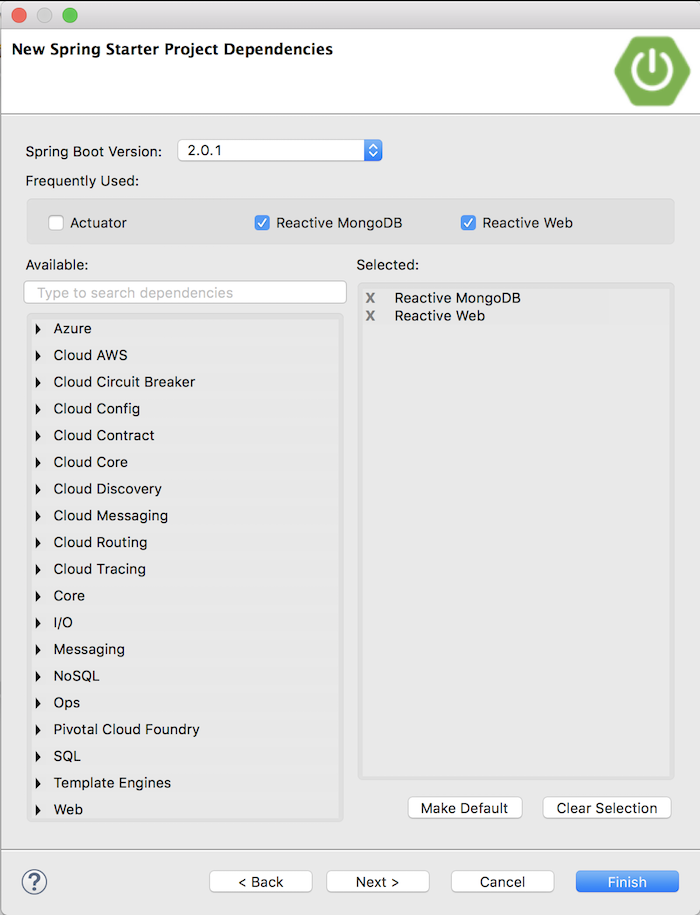
as an example.
Result:
Project Lombok:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.16.20</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> |
In this example, I will create an application that allows users to add new student information and get a list of students with data stored in the MongoDB database. When a user requests to our application, whenever a new student is added, the student’s information is published to the user.
Before going into the main content of the tutorial, there are 2 things I need to tell will you all first.
First, I will tell you some information about Spring Data MongoDB Reactive.
Similar to Spring Data MongoDB, an interface named ReactiveMongoRepository was introduced in Spring Data MongoDB Reactive. We have the Repository interface as the main interface in the Spring Data project. And with the Reactive model, we have the ReactiveCrudRepository interface, ReactiveSortingRepository extends from the Repository interface to serve this model. And the Spring Data MongoDB Reactive’s ReactiveMongoRepository interface extends from the ReactiveSortingRepository interface. You will see this through the following image:
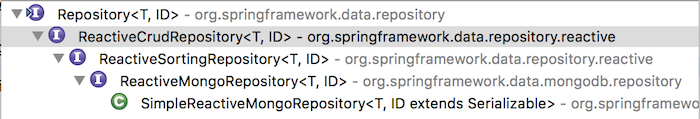
As you can see, the implementation of the ReactiveMongoRepository interface is the SimpleReactiveMongoRepository class.
The second is for our application to push student information whenever it is added, we need to use MongoDB with the capped collection.
The reason is that by default, for each query, when the user has exhausted the data for that query, MongoDB closes the cursor. Cursor in MongoDB you can understand that it is a pointer in a result set of a query. MongoDB’s close cursor makes it impossible to continue receiving data from our query.
To solve this problem, we will use the tailable cursor with MongoDB’s capped collection. Capped collections are fixed-size collections, meaning we can only add a certain number of documents. When the capped collection is full, the new document will override the oldest document. For the tailable cursor, if you used the tail -f command in Linux, you can imagine that tailable cusor will keep retrieving document after the user has retrieved the result for the query.
You can create a capped collection using the following command in the MongoDB Shell:
|
1 |
db.createCollection( "<collection_name>", { capped: true, size: <collection_size> } ) |
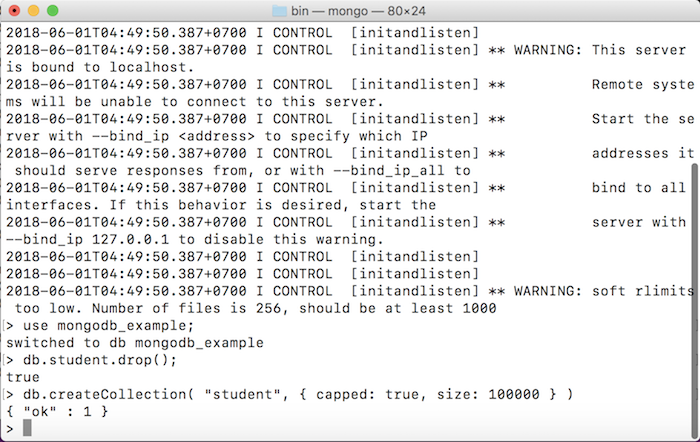
In the example of this tutorial, I will create a capped collection named student as follows:
|
1 |
db.createCollection( "student", { capped: true, size: 100000 } ) |
Result:
OK, now we will go into the main example of this tutorial.
First, I will create an interface named StudentRepository extends from Reactive MongoRepository with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package com.huongdanjava.springwebfluxmongodb; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.ReactiveMongoRepository; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Tailable; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; public interface StudentRepository extends ReactiveMongoRepository<Student, String> { @Tailable Flux<Student> findBy(); } |
The Student class has the following contents:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package com.huongdanjava.springwebfluxmongodb; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; @Setter @Getter public class Student { private String name; private String age; } |
As you can see, although ReactiveMongoRepository has provided us with the findAll() method to retrieve all student lists, but this method does not support the tailable cursor, we must define a findBy() method. It has the same functionality as the findAll() method with the @Tailable annotation. The findBy() method will allow us to use the tailable cursor function to keep retrieving document after the user has retrieved the result of the query.
Next, I will configure the connection to the MongoDB server.
Since our example project is a Spring Boot project, it is much simpler to configure the connection to the MongoDB server. We will not need to instantiate the MongoTemplate object. To do this, open the application.properties file and depending on whether you are using MongoDB server with authentication mode or not, configure as below.
For authenticate mode, we need to declare the username and password as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 |
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://<host>:<port>/<database_name> spring.data.mongodb.username=<username> spring.data.mongodb.password=<password> |
Otherwise just declare:
|
1 |
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://<host>:<port>/<database_name> |
is to be.
Currently, I use MongoDB server without username, password so I just declare as follows:
|
1 |
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/mongodb_example |
The last thing we need to do is add Controller to expose 2 requests: a request that allows the user to retrieve the student list and a request that allows the user to add new student.
I will create StudentController with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com.huongdanjava.springwebfluxmongodb; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; @RestController public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @GetMapping(value = "/students", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE) public Flux<Student> findAllStudents() { return studentRepository.findBy(); } @PostMapping("/student") public Mono<Student> createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) { return studentRepository.save(student); } } |
As you can see, I have built 2 requests: “/students” with the GET method and produces “text/event-stream” which allows users to retrieve all student lists and whenever new students are added, this student’s information will be pushed down to the user; “/student” with the POST method allows us to add new student.
The ReactiveMongoRepository has provided us with the findAll() and save() methods, so we just call them for use. One point to note is that, instead of returning to a List<Student> as in Spring Data MongoDB does, here Spring Data MongoDB Reactive will return a Flux<Student> object and similarly the save() method. Also, it returns a Mono<Student> object.
OK, here we have completed the necessary steps to build this example application. Try it now.
I will open a browser window to run the “/students” request and use Postman to run the request “/student” to add a new student.
I will use Postman to add new student first:
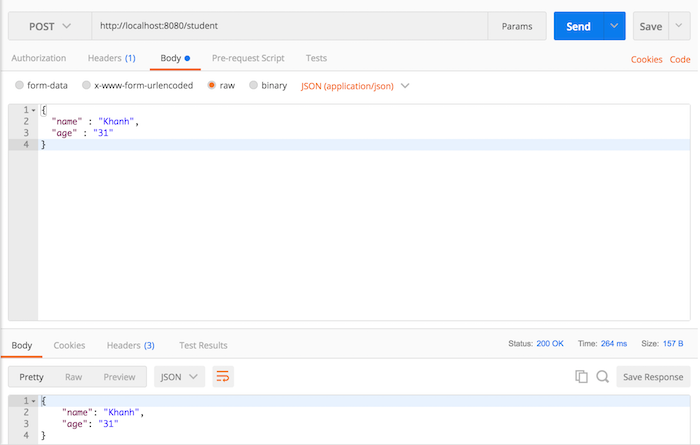
At this time, the request “/students” will have the following output:
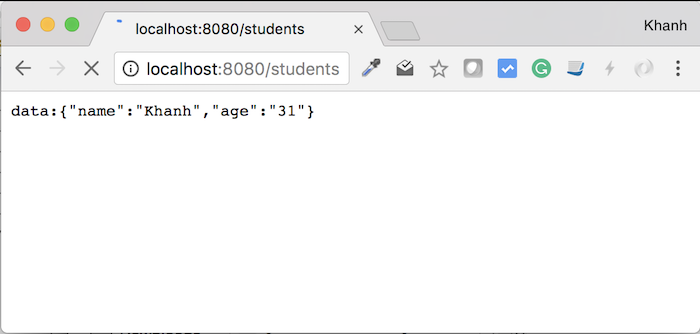
Now, if you add another student:
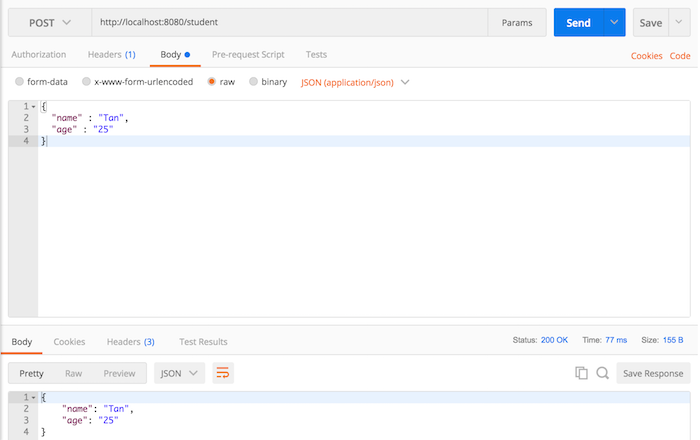
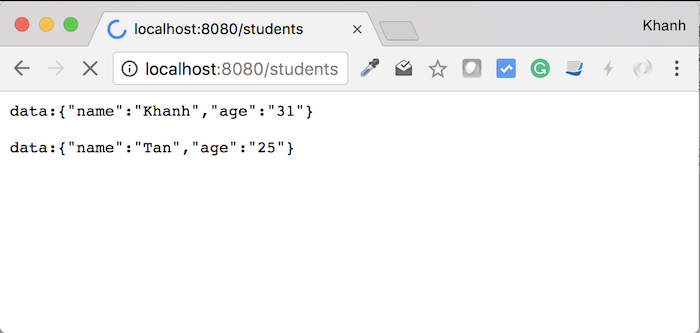
As you will see, the student’s information is automatically pushed to the browser window with the “/students” request.




Venkat Vinjamuri
Good article. Looks like Tailable cursor works only for new records. Does it work for document updates?