The ThreadLocal class in Java is a class that allows us to store and retrieve the values of variables in the same thread. As long as it’s the same thread, you can store a value and retrieve it whenever we want.
You can initialize objects of the ThreadLocal class normally like other classes as follows:
|
1 |
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); |
You should clearly specify the data type that the ThreadLocal object will store. In the example above, I declared the data type that the ThreadLocal object will store as String!
Now you can use the set() method of this ThreadLocal object to store the value you want, for example:
|
1 |
threadLocal.set("Huong Dan Java"); |
To get this value, you can use the get() method as follows:
|
1 |
threadLocal.get() |
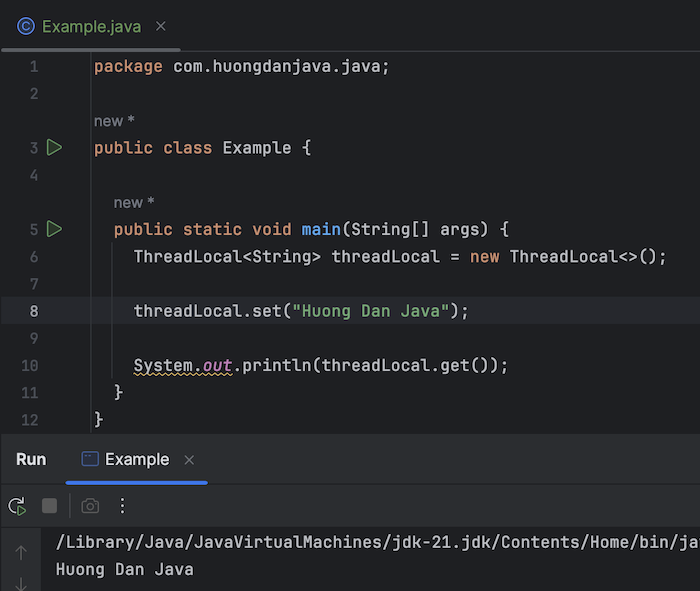
Results when I run the example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); threadLocal.set("Huong Dan Java"); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); } } |
will be as follows:
 If you retrieve the value stored in ThreadLocal in another thread, you will see that the value will be null. Because two different threads will not see the value in each other’s ThreadLocal. For example, if I write more code to read the value of ThreadLocal that I created above:
If you retrieve the value stored in ThreadLocal in another thread, you will see that the value will be null. Because two different threads will not see the value in each other’s ThreadLocal. For example, if I write more code to read the value of ThreadLocal that I created above:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); threadLocal.set("Huong Dan Java"); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Getting value from another thread: " + threadLocal.get()); } }); thread.start(); } } |
then when you run it, you will see the following results:
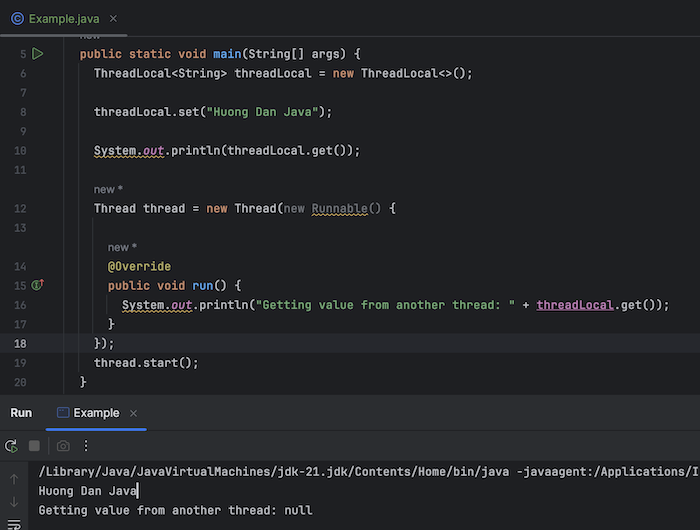
My example has 2 threads: one is the main thread running the application and a new thread that I create. As you can see, the newly created thread does not see the value stored in the main thread’s ThreadLocal.
You can remove the value stored in ThreadLocal using the remove() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); threadLocal.set("Huong Dan Java"); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); threadLocal.remove(); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); } } |
The result when I run the example will be as follows:
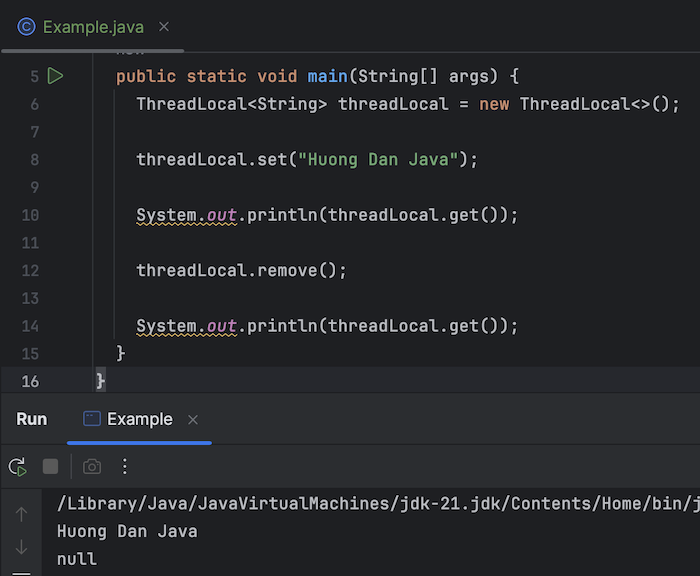
After removing, there are no more values stored in ThreadLocal!


