In the previous tutorial, I introduced you all about Constructor Injection in Spring. But because we can have overloaded constructors in Java, so in this tutorial, I will show you all how we can declare those overloaded constructors in the Spring container.
Let’s consider the following example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com.huongdanjava.springoverloadedconstructorinjection; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(String name) { this.name = name; } public Student(int age) { this.age = age; } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } } |
As you see, the Student object has 3 constructors, 2 of them are overloaded constructors. Now, we will consider each case!
But first of all, I will create a new Maven project:
I will use Java 17 for this example application:
|
1 2 3 4 |
<properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> </properties> |
Spring dependency is as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>6.0.2</version> </dependency> |
The Application class has the content below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
package com.huongdanjava.springoverloadedconstructorinjection; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { BeanFactory context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student.toString()); } } |
OK, let’s get started.
With overloaded constructors, we need to specify the data type for each argument in the constructor.
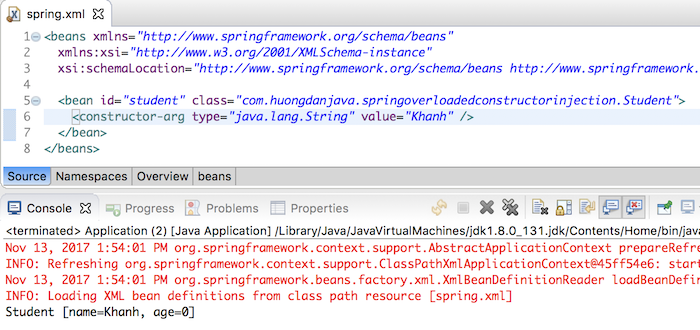
For example, I want to initialize a Student object with the name “Khanh”. I will declare in Spring container as below:
|
1 2 3 |
<bean id="student" class="com.huongdanjava.springoverloadedconstructorinjection.Student"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="Khanh" /> </bean> |
With this declaration, Spring will call the constructor:
|
1 2 3 |
public Student(String name) { this.name = name; } |
to initialize the Student object because the data type of the name variable is String.
Result:
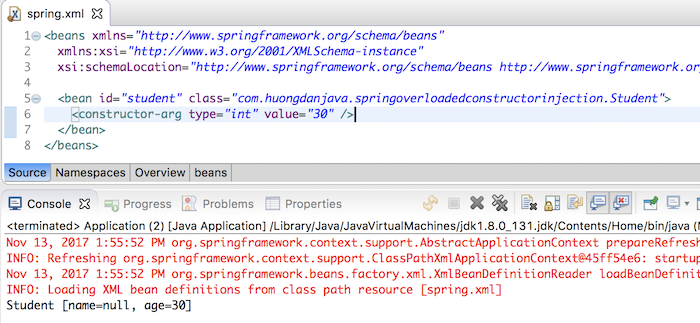
If now I want to initialize the Student object with an age is 30, then I need to change the data type as below:
|
1 2 3 |
<bean id="student" class="com.huongdanjava.springoverloadedconstructorinjection.Student"> <constructor-arg type="int" value="30" /> </bean> |
Now, Spring will call the constructor:
|
1 2 3 |
public Student(int age) { this.age = age; } |
to initialize the Student object and the result will be as below:
With the constructor has many arguments, we declare it as normal:
|
1 2 3 4 |
<bean id="student" class="com.huongdanjava.springoverloadedconstructorinjection.Student"> <constructor-arg value="Khanh" /> <constructor-arg value="30" /> </bean> |



faisal
XML based configuration …. yuk!