In our previous tutorials, we looked at an overview about the Spring Boot and how to create a Spring Boot project using the CLI, using the Spring Initialzr Web and the Spring Tool Suite. Some of you who have not worked much with Spring Boot will wonder how it works. So, in this tutorial, I will take a moment to talk about how Spring Boot works for you. If you already know, then review again to see if you understand correctly.
OK, I will first create a new Spring Boot project with Web Starter and a HelloController class as follows:
The contents of the HelloController class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping(value = "/") public ResponseEntity<String> hello() { return new ResponseEntity<>("Hello World!", HttpStatus.OK); } } |
Now, if you run this project and access the http://localhost:8080/ path, you will see the following output:
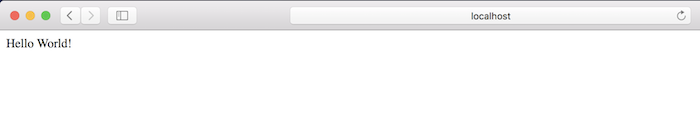
As you can see, although we do not declare necessary configuration files like web.xml, @Configuration annotation, or any bean in the Spring container, our application is still running normally and displaying the content that we want.
To do this, Spring Boot must rely on the @SpringBootApplication annotation declared in the SpringBootExampleApplication class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootExampleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootExampleApplication.class, args); } } |
This annotation allows Spring Boot to automatically scan all of the configurations and beans in our application.
The content of this annotation is as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 |
/* * Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationBeanNameGenerator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor; import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository; /** * Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more * {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration * auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience * annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration}, * {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Andy Wilkinson * @since 1.2.0 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { /** * Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied. * @return the classes to exclude */ @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class) Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; /** * Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be * applied. * @return the class names to exclude * @since 1.3.0 */ @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class) String[] excludeName() default {}; /** * Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses} * for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names. * <p> * <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for * {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity} * scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add * {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and * {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations. * @return base packages to scan * @since 1.3.0 */ @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages") String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; /** * Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to * scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned. * <p> * Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that * serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute. * <p> * <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for * {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity} * scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add * {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and * {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations. * @return base packages to scan * @since 1.3.0 */ @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses") Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; /** * The {@link BeanNameGenerator} class to be used for naming detected components * within the Spring container. * <p> * The default value of the {@link BeanNameGenerator} interface itself indicates that * the scanner used to process this {@code @SpringBootApplication} annotation should * use its inherited bean name generator, e.g. the default * {@link AnnotationBeanNameGenerator} or any custom instance supplied to the * application context at bootstrap time. * @return {@link BeanNameGenerator} to use * @see SpringApplication#setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator) * @since 2.3.0 */ @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "nameGenerator") Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; /** * Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce * bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in * case of direct {@code @Bean} method calls in user code. This feature requires * method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which * comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being * allowed to declare {@code final}. * <p> * The default is {@code true}, allowing for 'inter-bean references' within the * configuration class as well as for external calls to this configuration's * {@code @Bean} methods, e.g. from another configuration class. If this is not needed * since each of this particular configuration's {@code @Bean} methods is * self-contained and designed as a plain factory method for container use, switch * this flag to {@code false} in order to avoid CGLIB subclass processing. * <p> * Turning off bean method interception effectively processes {@code @Bean} methods * individually like when declared on non-{@code @Configuration} classes, a.k.a. * "@Bean Lite Mode" (see {@link Bean @Bean's javadoc}). It is therefore behaviorally * equivalent to removing the {@code @Configuration} stereotype. * @since 2.2 * @return whether to proxy {@code @Bean} methods */ @AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class) boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; } |
@SpringBootApplication annotation is a combination of three other Spring annotations, including @SpringBootConfiguration, @ComponentScan, and @EnableAutoConfiguration where the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation is the most important.
With @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation, Spring Boot will automatically configure our application based on the classpath, annotations, and configuration information that we defined.
All of these annotations will help the Spring Boot automatically configure our applications accordingly and we do not need to worry about configuring them.
In our example, Spring Boot checks the classpath in our project, and because of its dependency on having spring-boot-starter-web, Spring Boot will be configured the application as a web application.
In addition, Spring Boot will treat its HelloController as a web controller based on the @Controller annotation and the @RequestMapping annotation.
By default, Spring Boot will use the Tomcat server to run the web application, so you will see some log mentions about the Tomcat server when you run this example application. You can change the Server runtime if you want!


