In the previous tutorial, I showed you how to enable API Versioning for the request header in a Spring application. In this tutorial, we will continue to learn how to enable API Versioning for the path parameter!
I will also create a new Spring Boot project with Spring Web dependency as follows:
As I also noted to you in the previous tutorial, we also need to use Spring Boot 4 with Spring Framework 7 and later!
Previously, when we needed to define a version for an endpoint in Spring MVC using a path parameter, we would define it with the endpoint URL, for example, as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/v1.0.0/hello") public String hello() { return """ { "message": "Hello from Huong Dan Java!" } """; } } |
With API versioning support from Spring Framework 7, defining versions for endpoints will be easier and more flexible.
To enable versioning for endpoints with path parameters, similar to the request header, you also need to implement the WebMvcConfigurer interface, override the configureApiVersioning() method, and use the usePathSegment() method as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ApiVersionConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; @Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void configureApiVersioning(ApiVersionConfigurer configurer) { configurer.usePathSegment(0) .setDefaultVersion("1.0.0"); } } |
The value of the parameter in the usePathSegment() method is the segment containing the version information in the endpoint. There are endpoints such as /v1.0.0/hello where the segment value is 0, while the /api/v1.0.0/hello endpoint has the segment value of 1, so depending on your needs, please pass the correct segment value! For my example, the segment will have a value of 0.
Here, I also use the setDefaultVersion() method to define the default version for endpoints that do not define version information.
With Spring Boot projects, instead of implementing the WebMvcConfigurer interface, you can also use the following properties:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
spring: mvc: apiversion: use: path-segment: 0 default: 1.0.0 |
To specify the version for any endpoint, you can use the version attribute of the annotations @GetMapping, @PostMapping, …. For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/v{version}") public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return """ { "message": "Hello from Huong Dan Java!" } """; } @GetMapping(value = "/hello", version = "1.1.0") public String hello1_1() { return """ { "message": "Hello from Huong Dan Java! V1.1.0" } """; } } |
Here, I also annotate the HelloController class with the @RequestMapping annotation to define the prefix for all endpoints in this class, starting with “/v{version}”.
Now, if you run the application and request to the /v1.0.0/hello endpoint, the result you will see is as follows:
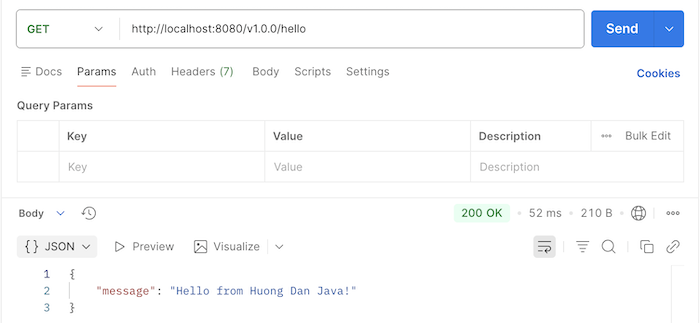
As you can see, the hello() method in the HelloController class will handle the request because it does not have a version defined, so by default it will be assigned version 1.0.0.
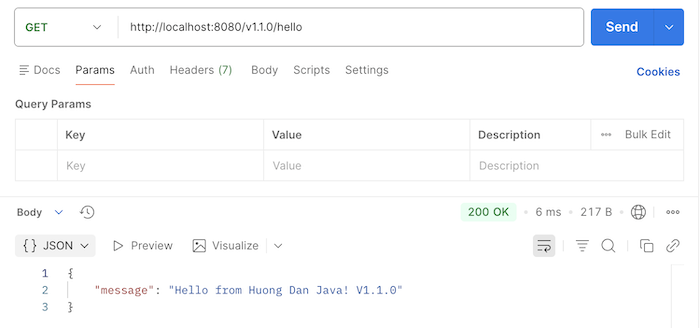
If the request goes to the endpoint /v1.1.0, the result will be as follows: