Since version 7, Spring has introduced another way for us to register one or more beans at the same time in the Spring container using the implementation of the BeanRegistrar interface. How exactly? Let’s find out in this tutorial!
I will create a Maven project:
with Spring Framework dependency:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>7.0.1</version> </dependency> |
for example.
Suppose I have a Hello class like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring; public class Hello { public void say() { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } } |
To register a bean for this Hello class using the implementation of the BeanRegistrar interface, you can override the register() method of the BeanRegistrar interface and use the registerBean() method of the BeanRegistry class as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanRegistrar; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanRegistry; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; public class HDJBeanRegistrar implements BeanRegistrar { @Override public void register(BeanRegistry registry, Environment env) { registry.registerBean(Hello.class); } } |
With the parameter of class Hello.class as above, Spring will automatically generate a unique bean name based on the class name and initialize the bean for class Hello in the Spring container.
You can assign the bean name you want, or you can also add conditions to initialize the bean for class Hello, for example, as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanRegistrar; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanRegistry; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; public class HDJBeanRegistrar implements BeanRegistrar { @Override public void register(BeanRegistry registry, Environment env) { registry.registerBean(Hello.class); registry.registerBean("huongdanjava_hello", Hello.class); if (env.matchesProfiles("dev")) { registry.registerBean("huongdanjava_hello_dev", Hello.class); } } } |
After implementing the BeanRegistrar interface, you can use the @Import annotation to declare this bean definition with the Spring container, as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; @Configuration @Import(HDJBeanRegistrar.class) public class AppConfig { } |
Now you can get the bean of the Hello class and use it:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
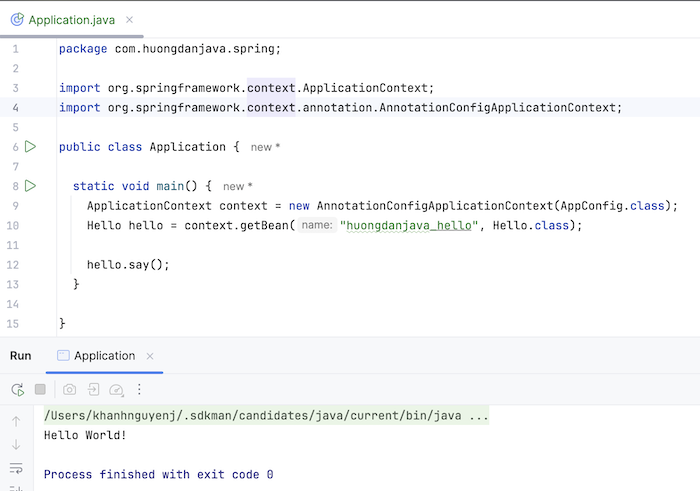
package com.huongdanjava.spring; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Application { static void main() { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); Hello hello = context.getBean("huongdanjava_hello", Hello.class); hello.say(); } } |
My results are as follows: