This method was introduced from Java 9.
This method is similar to the ifPresent() method which I introduced in this tutorial, but here is a difference since we have one more Runnable parameter, so that in-case if the Optional object is empty, the object of the Runnable interface will be executed.
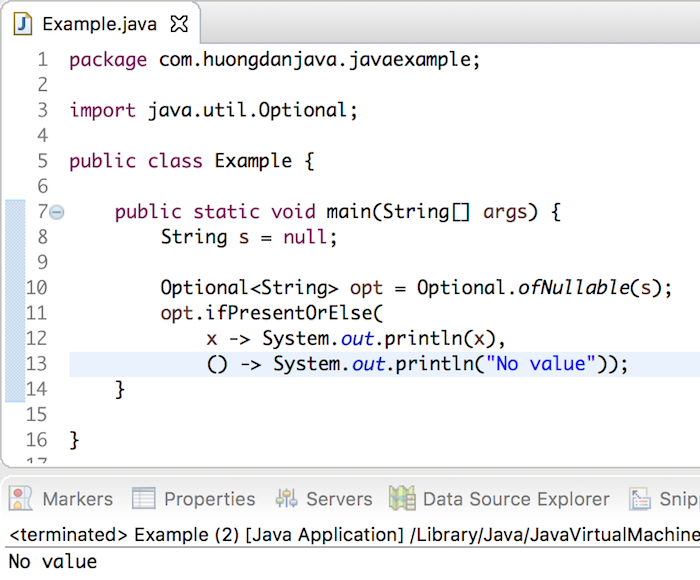
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package com.huongdanjava.javaexample; import java.util.Optional; public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = null; Optional<String> opt = Optional.ofNullable(s); opt.ifPresentOrElse( x -> System.out.println(x), () -> System.out.println("No value")); } } |
Result: