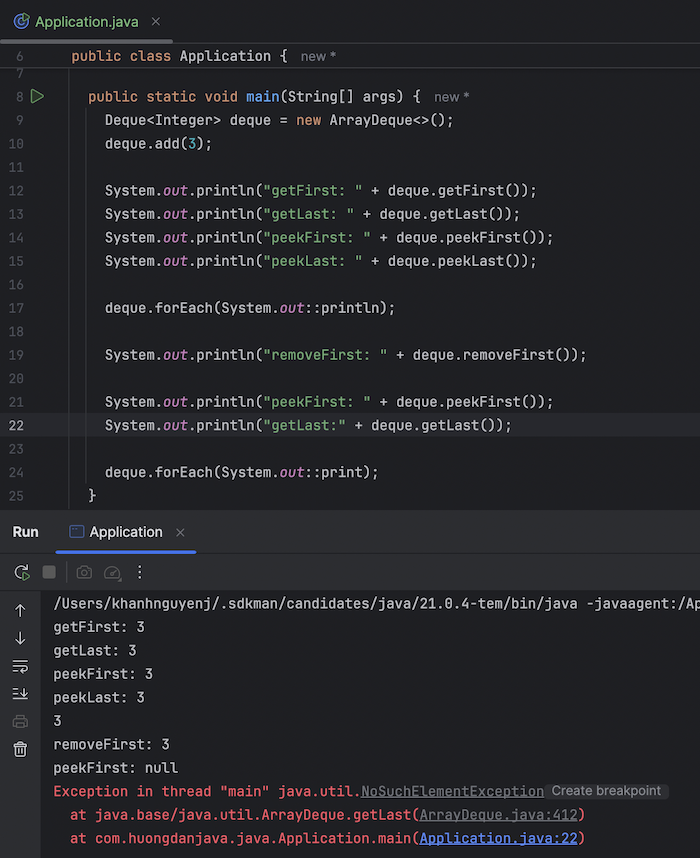
Interface Deque (short for Double-Ended Queue) in Java is an interface that defines a data structure that allows us to add or remove elements at the front or rear:
You can watch the videos below:
and:
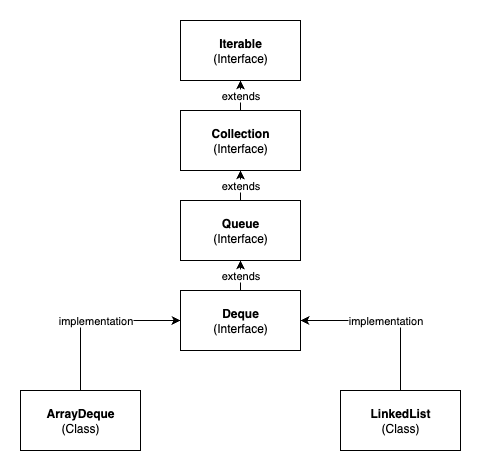
This Deque interface extends from the Queue interface and it has 2 main implementations: ArrayQueue and LinkedList, as follows:
We can use Deque to implement:
- Stack with LIFO (Last In First Out): add elements and remove elements from the front
- or Queue with FIFO (First In First Out): add elements from the rear, remove elements from the front
To work with Deque, you can use some of its methods as follows:
Table of Contents
addFirst() and addLast() methods
- addFirst(E e): add element at the front.
- addLast(E e): add element at the rear.
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Deque; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); deque.add(3); deque.addFirst(1); deque.addLast(2); deque.forEach(System.out::print); } } |
The add() method is similar to the addLast() method! The push() method is similar to the addFirst() method!
In the above example, initially, my deque only has 3 elements. Using the addFirst() and addLast() methods, I can add more elements to the beginning and end. The result is as follows:
offerFirst() and offerLast() methods
The two methods offerFirst() and offerLast() are similar to the two methods addFirst() and addLast(), but the difference is that if your collection has capacity. Adding new elements may not be possible when your collection is full capacity.
- offerFirst(E e): add elements to the front, if it cannot be added, it will return false, otherwise it will return true.
- offerLast(E e): add elements to the rear, similar to offerFirst(), it will return false if it cannot be added, otherwise it will return true.
With the two implementations, ArrayQueue or LinkedList, the size of the collection will automatically increase, so when you use the two methods offerFirst() and offerLast(), the result will always return true!
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Deque; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(1); deque.add(3); System.out.println(deque.offerFirst(1)); System.out.println(deque.offerLast(2)); deque.forEach(System.out::print); } } |
Result:

As you can see, although I only initialized the ArrayDeque object with a capacity of 1, this object can automatically increase its capacity and save all the elements that I added using the offer methods, without any errors.
removeFirst(), pollFirst(), removeLast() and pollLast() methods
The two methods removeFirst() and pollFirst() remove and return the element at the beginning of the collection. The difference is that if there is no element to remove, removeFirst() will throw java.util.NoSuchElementException, while pollFirst() will return null.
Similarly, the methods removeLast() and pollLast() remove and return the element at the end of the collection. The difference is that if there is no element to remove, removeLast() will throw java.util.NoSuchElementException, while pollLast() will return null.
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Deque; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); deque.add(3); deque.add(2); System.out.println(deque.removeFirst()); System.out.println(deque.pollFirst()); System.out.println(deque.pollLast()); System.out.println(deque.removeLast()); deque.forEach(System.out::print); } } |
Result:
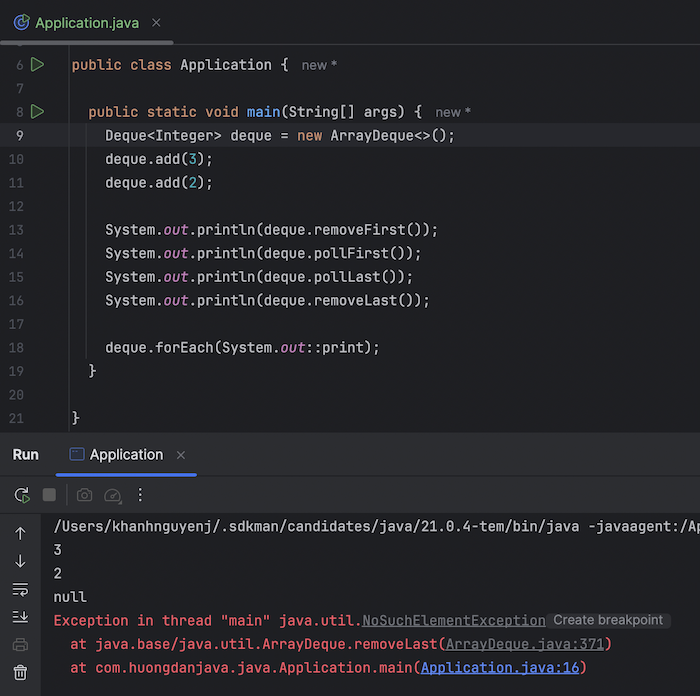
The poll() method is similar to the pollFirst() method!
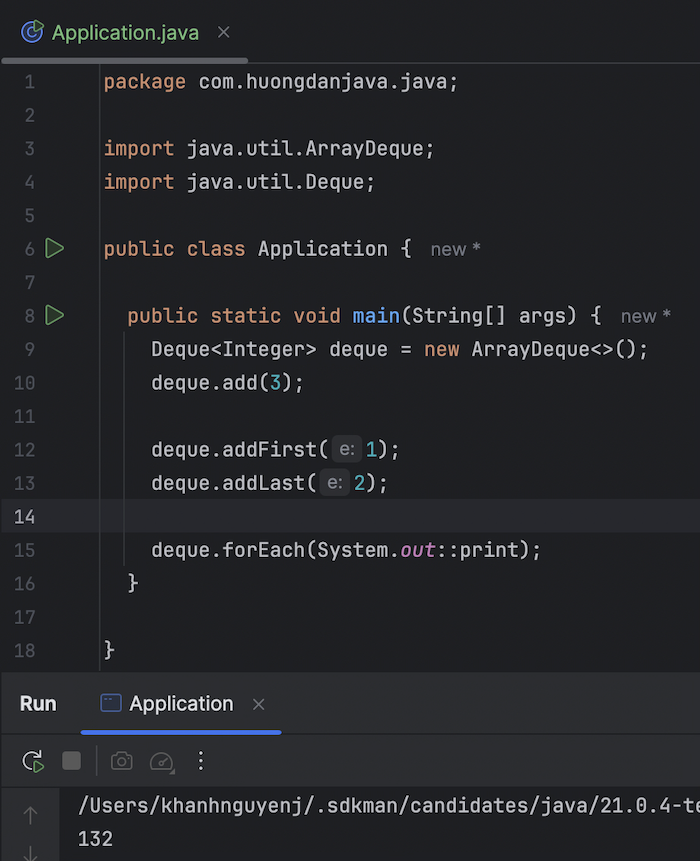
getFirst(), peekFirst(), getLast() and peekLast() methods
The getFirst() and peekFirst() methods will only return the element at the front without removing it. The difference is that if there is no element to return, getFirst() will throw java.util.NoSuchElementException, while peekFirst() will return null.
The same goes for the getLast() and peekLast() methods!
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
package com.huongdanjava.java; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Deque; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); deque.add(3); System.out.println("getFirst: " + deque.getFirst()); System.out.println("getLast: " + deque.getLast()); System.out.println("peekFirst: " + deque.peekFirst()); System.out.println("peekLast: " + deque.peekLast()); deque.forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("removeFirst: " + deque.removeFirst()); System.out.println("peekFirst: " + deque.peekFirst()); System.out.println("getLast:" + deque.getLast()); deque.forEach(System.out::print); } } |
Result: