If your application uses Spring Framework 7 or later, you can now use the RestClient class to consume RESTful APIs. How exactly? Let’s find out in this tutorial!
For example, I will create a new Spring Boot project version 4.0.0 or later, using the Web Starter dependency as follows:
I will consume 2 APIs that I have exposed in 2 tutorials about API Versioning using request header and path parameter, guys!
For example, to keep it simple, I will also use the CommandLineRunner class so that when running the Spring Boot application, it will call the 2 APIs above using the RestClient class.
You can initialize the RestClient class object with baseURL as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootRestClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestClientApplication.class, args); } @Bean CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) { return args -> { RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder() .baseUrl("http://localhost:8080") .build(); }; } } |
Suppose the RESTful API you need to consume uses API Versioning, like the example in the tutorial API Versioning using request headers with Spring framework. In that case, you can use the ApiVersionInserter class to add version information, for example, as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.client.ApiVersionInserter; import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootRestClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestClientApplication.class, args); } @Bean CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) { return args -> { ApiVersionInserter apiVersionInserter = ApiVersionInserter.builder() .useHeader("X-Api-Version") .build(); RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder() .baseUrl("http://localhost:8080") .apiVersionInserter(apiVersionInserter) .build(); }; } } |
Because the API in the tutorial API Versioning using request headers with Spring framework using headers for API versioning, you can use the useHeader() method of the ApiVersionInserter class to add header name information. The value of this header name will be declared when we call the “/hello” endpoint as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
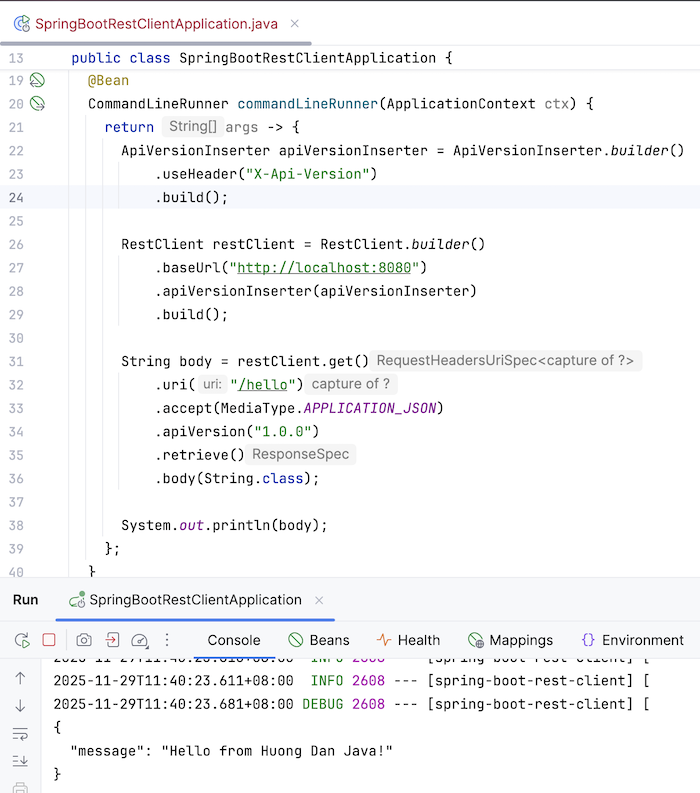
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.client.ApiVersionInserter; import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootRestClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestClientApplication.class, args); } @Bean CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) { return args -> { ApiVersionInserter apiVersionInserter = ApiVersionInserter.builder() .useHeader("X-Api-Version") .build(); RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder() .baseUrl("http://localhost:8080") .apiVersionInserter(apiVersionInserter) .build(); String body = restClient.get() .uri("/hello") .accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) .apiVersion("1.0.0") .retrieve() .body(String.class); System.out.println(body); }; } } |
As you can see, we use the apiVersion() method to pass the endpoint version information.
The result when you run this example is as follows:
If you request the API in the tutorial API Versioning using path parameter with Spring framework, you can use the usePathSegment() method of the ApiVersionInserter class to define a segment containing version information as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
package com.huongdanjava.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.client.ApiVersionInserter; import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootRestClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestClientApplication.class, args); } @Bean CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) { return args -> { ApiVersionInserter apiVersionInserter = ApiVersionInserter.builder() .usePathSegment(0) .build(); RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder() .baseUrl("http://localhost:8080") .apiVersionInserter(apiVersionInserter) .build(); String body = restClient.get() .uri("/hello") .accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) .apiVersion("v1.0.0") .retrieve() .body(String.class); System.out.println(body); }; } } |
The result when I run this example is as follows:



