In the previous tutorial, I introduced to you all the basic operations with MongoDB using Java. If your application is using Spring framework, make use of a Spring library for MongoDB to manipulate this database system. How is it in details? Let’s find out in this tutorial!
First, I will create a new Maven project as an example:
The library mentioned above is called spring-data-mongodb. I will add its dependency as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-mongodb</artifactId> <version>2.0.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> |
The main interface for manipulating MongoDB in the spring-data-mongodb library is the MongoOperations interface. It defines many different ways that we can easily manipulate MongoDB. The main class implements the MongoOperations interface named MongoTemplate, and to use the MongoOperations interface, we need to declare the bean for the MongoTemplate class in the Spring container.
I will create a configuration file for Spring located in src/main/resources named spring.xml with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> </beans> |
Class MongoTemplate has 3 constructors, see here for more! You can choose any constructor to initialize object for MongoTemplate. Here, I will initialize the MongoTemplate with a MongoClient object with the database name: MongoTemplate(com.mongodb.MongoClient mongoClient, String databaseName).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="mongoTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate"> <constructor-arg ref="mongoClient" /> <constructor-arg value="mongodb_example" /> </bean> </beans> |
We need to initialize the bean for the MongoClient object.
If your MongoDB does not need a username, password then you can initialize the MongoClient object as follows:
|
1 |
<bean id="mongoClient" class="com.mongodb.MongoClient" /> |
in case your MongoDB installs locally and uses its default port.
In case MongoDB is installed on another machine, you can initialize the MongoClient object as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 |
<bean id="mongoClient" class="com.mongodb.MongoClient"> <constructor-arg value="10.29.19.22"/> <constructor-arg value="27017" /> </bean> |
If your MongoDB needs username and password then you can use the constructor MongoClient(ServerAddress addr, List<MongoCredential> credentialsList) to initialize it:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
<bean id="mongoClient" class="com.mongodb.MongoClient"> <constructor-arg ref="mongoServerAddress" /> <constructor-arg ref="mongoCredentialList" /> </bean> <bean id="mongoServerAddress" class="com.mongodb.ServerAddress"> <constructor-arg value="localhost" /> <constructor-arg value="27017" /> </bean> <bean id="mongoCredential" class="com.mongodb.MongoCredential"> <constructor-arg value="khanh" /> <constructor-arg value="mongodb_example" /> <constructor-arg value="abc123" /> </bean> <bean id="mongoCredentialList" class="java.util.ArrayList"> <constructor-arg> <list> <ref bean="mongoCredential" /> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean> |
In the example of this tutorial, I installed MongoDB locally and did not need a username or password, so I just initialized the MongoClient object as follows:
|
1 |
<bean id="mongoClient" class="com.mongodb.MongoClient" /> |
Here we have finished configuring to work with MongoDB in Spring. Now let’s take an example!
I have a Student object as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring.mongodb; import org.bson.Document; public class Student extends Document { private static final String NAME = "name"; private static final String AGE = "age"; public static final String COLLECTION_NAME = "student"; public String getName() { return getString(NAME); } public void setName(String name) { put(NAME, name); } public Integer getAge() { return getInteger(AGE); } public void setAge(Integer age) { put(AGE, age); } } |
Insert a document:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
package com.huongdanjava.spring.mongodb; import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection; import org.bson.Document; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoOperations; public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); MongoOperations mo = (MongoOperations) ac.getBean("mongoTemplate"); MongoCollection<Document> studentCollection = mo.getCollection(Student.COLLECTION_NAME); Student student = new Student(); student.setName("Khanh"); student.setAge(31); studentCollection.insertOne(student); } } |
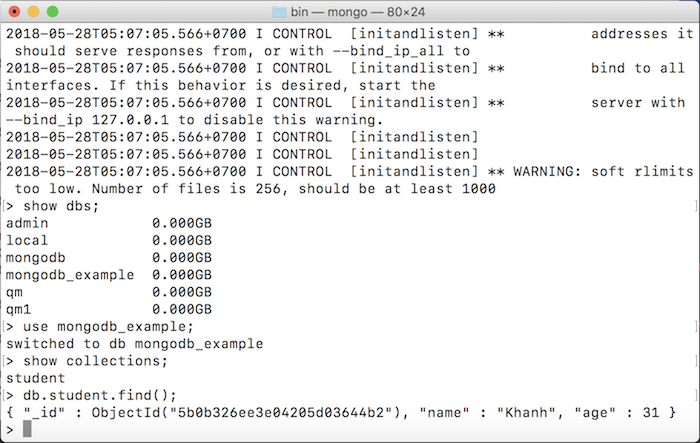
Result: