Check out the full series of Questions Management tutorial here.
Before we go into building the first API for the Core Option Service, we need to prepare the following:
First, we need to create an OptionRepository interface extends from the ReactiveMongoRepository interface to manipulate the MongoDB database.
The contents of the OptionRepository interface will look like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
package com.huongdanjava.optionservice.repository; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.ReactiveMongoRepository; import com.huongdanjava.optionservice.document.Option; public interface OptionRepository extends ReactiveMongoRepository<Option, String> { } |
with the Option document object:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
package com.huongdanjava.optionservice.document; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document; import lombok.Data; @Data @Document public class Option { private String id; private String description; private String note; private Boolean isCorrect; private String questionId; } |
You can see the tutorial Reactive REST APIs with Spring Data MongoDB Reactive and Spring WebFlux for more information.
Next I will configure the connection to the MongoDB server.
Currently I am using MongoDB server without authentication mode so I just declare the following in application.properties file:
|
1 |
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/qm |
I will run this service using port 8083 so I will add the server.port property in the application.properties file as follows:
|
1 |
server.port=8083 |
OK, everything is ready, now we will go to the main part of this tutorial.
I will create a controller named OptionController with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
package com.huongdanjava.optionservice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/option") public class OptionController { } |
With this declaration, I expose APIs for the Core Option Service with the request URL starting with “/option”.
To work with MongoDB server, we need to inject OptionRepository into OptionController class as follows:
|
1 2 |
@Autowired private OptionRepository optionRepository; |
To build API to add a new option, I will add a method to expose a POST request “/add” with data in the body as the Option document object:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@PostMapping("/add") public Mono<Option> createOption(@RequestBody Option option) { } |
Because Spring MongoDB Reactive has provided us with the save() method to save the data to MongoDB, we just need to call this method:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@PostMapping("/add") public Mono<Option> createOption(@RequestBody Option option) { return optionRepository.save(option); } |
At this point, we have completed the API to create a new option for the Core Option Service, let’s test it.
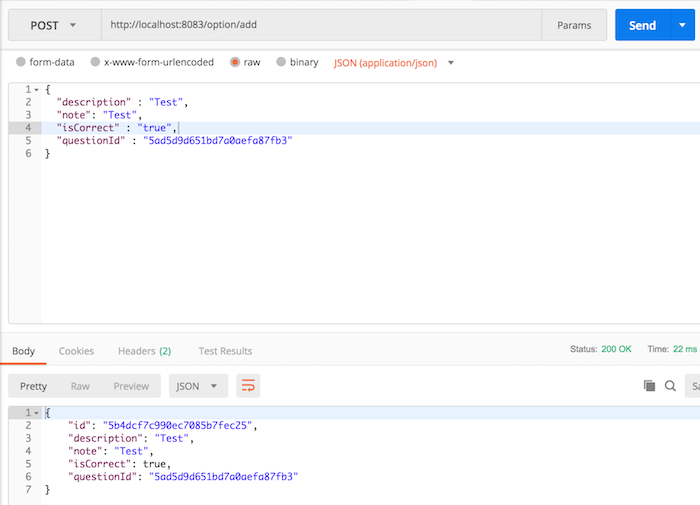
The last thing we need to do is add a new Unit Test to the code we just added.
I will create a new class called OptionControllerTest located in the src/test/java package to test the OptionController class.
Mock OptionRepository class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
package com.huongdanjava.optionservice; import org.mockito.Mock; import com.huongdanjava.optionservice.repository.OptionRepository; public class OptionControllerTest { @Mock private OptionRepository optionRepository; } |
Inject the mock object of the OptionRepository to the OptionController class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package com.huongdanjava.optionservice; import org.mockito.InjectMocks; import org.mockito.Mock; import com.huongdanjava.optionservice.repository.OptionRepository; public class OptionControllerTest { @Mock private OptionRepository optionRepository; @InjectMocks private OptionController optionController; } |
To use mock objects, we have to initialize them one by one so I will add a method with the JUnit @Before annotation as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@Before public void init() { MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); } |
The code to test the createOption() method is as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
@Test public void testCreateOptionn() { // Create document need to insert into MongoDB Option option = new Option(); option.setDescription("Test"); option.setNote("Test"); option.setIsCorrect(true); option.setQuestionId("123XYZ"); // The result should be the same with additional id field Option result = option; result.setId("123"); // Mock save() method of OptionRepository when(optionRepository.save(option)).thenReturn(Mono.just(result)); // Call method Mono<Option> createdOptionAsMono = optionController.createOption(option); Option createdOption = createdOptionAsMono.block(); // Assertions assertEquals("Test", createdOption.getDescription()); assertEquals("Test", createdOption.getNote()); assertEquals("123XYZ", createdOption.getQuestionId()); assertEquals(true, createdOption.getIsCorrect()); assertEquals("123", createdOption.getId()); } |
Run “Maven test” in STS or “mvn test” with Apache Maven, you will not see any errors.


