In Java, we have the following assignment operators:
- =
- +=
- -=
- *=
- /=
– The assignment operator “=” is used most often, which is used to initialize the variable and assign a new value to it.
Example:
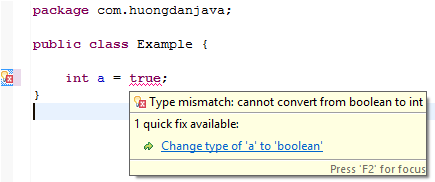
You cannot use this assignment operator to assign a boolean value to a variable of type char, byte, short, int, long or float, or double and vice versa. If you try to do that then the compile error will occur.
You cannot assign a variable whose data type has a larger range value to a variable whose value type has a smaller range value.
For example, we cannot assign a variable of type long to a variable of type int:
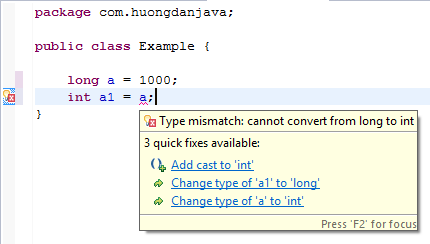
That’s because the range value of the long type is greater than int.
The remaining operators include “+ =”, “- =”, “* =”, “/ =” are abbreviations for summation, subtraction, multiplication and division with the assignment operator.
- “+=”: first plus then assign.
- “-=”: the first is the subtraction followed by the assignment.
- “*=”: first multiply then assign.
- “/=”: first divide then assign.
For example, we have the following calculation:
|
1 |
a += b; |
which means that
|
1 |
a = a + b; |
Or
|
1 |
a -= b; |
which means that
|
1 |
a = a - b |
Similarly to divide and multiply.


