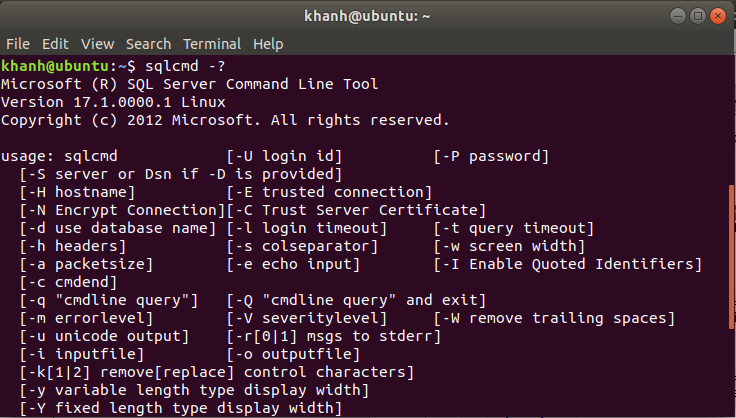
To be able to connect to an MSSQL Server in Ubuntu, we need to install the sqlcmd tool, which is a Microsoft tool. In this tutorial, I instruct you to install this tool.
First, just like installing MSSQL Server on Ubuntu, you also need to add the Microsoft certificate to your machine:
|
1 |
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - |
then add the Microsoft Ubuntu repository:
|
1 |
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/msprod.list |
Result:
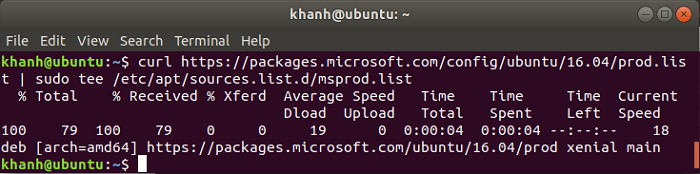
At this point, you need to run the command:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get update |
to update all the software available in your Ubuntu machine’s repository.
Now you can start installing the sqlcmd tool:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install mssql-tools |
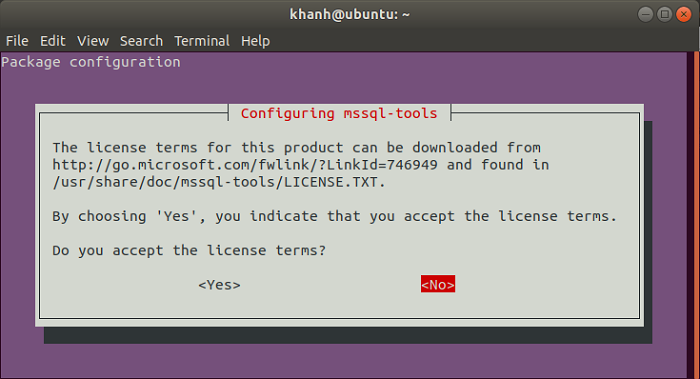
During installation, there will be some windows on terms of use for:
mssql-tools
msodbcsql17
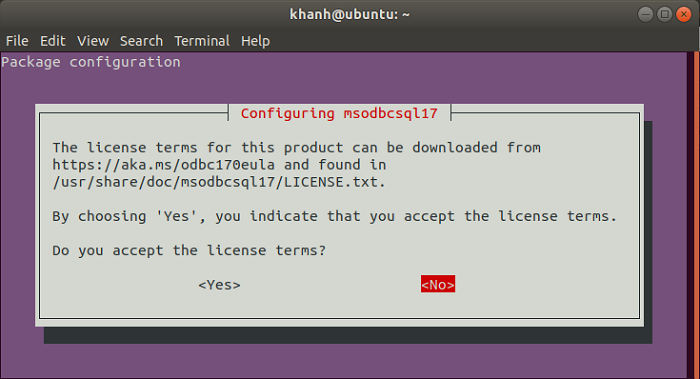
All you have to do is to select Yes.
Once the installation is complete, the location of the sqlcmd tool will be in the /opt/mssql-tools/bin/ directory. You can use this path to use the sqlcmd tool, for example to check the version of this tool as follows:
|
1 |
/opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd -? |
Result:
Or export the path /opt/mssql-tools/bin into the $PATH environment variable by adding the following at the end of the .bashrc file in the user directory:
|
1 |
export PATH=/opt/mssql-tools/bin:$PATH |
then run the following command to update:
|
1 |
. .bashrc |
Then, you can use the sqlcmd tool anywhere in your machine. Eg: