We had a look at how to read an XML file using the DOM in Java in the previous tutorial. This tutorial introduces you to another way to read XML file faster and use less memory than the DOM, which is using SAX in Java.
That’s because the way SAX works is so different from the DOM, it does not load the contents of an XML file into memory or create any object that holds information about the XML file. Instead, it uses the callback methods of the org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler object to read the XML file from top to bottom.
For you to understand more, I have the following example:
The contents of the XML file are as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?> <students> <student n0='1'> <name>John</name> <code>12345</code> <age>19</age> </student> <student n0='2'> <name>Marry</name> <code>23456</code> <age>24</age> </student> </students> |
Here, I use a Student object to store the readable information of the XML file, the contents of the Student class as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
package com.huongdanjava.sax; public class Student { private String name; private String age; private String code; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(String age) { this.age = age; } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", code=" + code + "]"; } } |
To read the XML file using SAX, we will first use the callback methods in the DefaultHandler object to read the XML file content. Imagine, we have an XML file and we will read its contents from top to bottom, from outside to inside following the hierarchical order.
The DefaultHandler object has the following callback methods:
- startDocument() and endDocument(): These two methods will be called when we start reading and finishing reading the XML file.
- startElement() and endElement(): These two methods are called when we start reading a tag in an XML file.
- characters(): This method is called when we read the content between the two tabs of an XML file.
I will write the DefaultHandler object to read the students.xml XML file as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
final List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>(); DefaultHandler defaultHandler = new DefaultHandler() { Student student = null; boolean isName = false; boolean isCode = false; boolean isAge = false; @Override public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException { if (qName.equals("student")) { student = new Student(); } else if (qName.equals("name")) { isName = true; } else if (qName.equals("code")) { isCode = true; } else if (qName.equals("age")) { isAge = true; } } @Override public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException { String value = new String(ch, start, length); if (isName) { student.setName(value); isName = false; } else if (isCode) { student.setCode(value); isCode = false; } else if (isAge) { student.setAge(value); isAge = false; } } @Override public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName) throws SAXException { if (qName.equals("student")) { students.add(student); } } }; |
Now that we have a handler object, we will initialize the SAXParser object to use the handler object to read the XML file.
|
1 2 |
SAXParserFactory saxParserFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance(); SAXParser saxParser = saxParserFactory.newSAXParser(); |
Next, we will call the parse() method of the SAXParser object to start reading the XML file.
|
1 |
saxParser.parse("students.xml", defaultHandler); |
View list of students after reading:
|
1 |
System.out.println(students.toString()); |
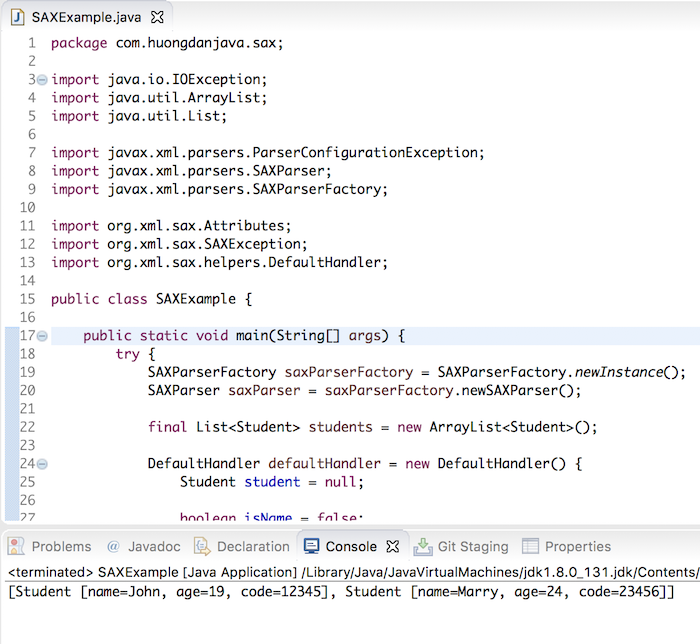
Result:
Full code for your reference:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 |
package com.huongdanjava.sax; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException; import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser; import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory; import org.xml.sax.Attributes; import org.xml.sax.SAXException; import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler; public class SAXExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { SAXParserFactory saxParserFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance(); SAXParser saxParser = saxParserFactory.newSAXParser(); final List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>(); DefaultHandler defaultHandler = new DefaultHandler() { Student student = null; boolean isName = false; boolean isCode = false; boolean isAge = false; @Override public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException { if (qName.equals("student")) { student = new Student(); } else if (qName.equals("name")) { isName = true; } else if (qName.equals("code")) { isCode = true; } else if (qName.equals("age")) { isAge = true; } } @Override public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException { String value = new String(ch, start, length); if (isName) { student.setName(value); isName = false; } else if (isCode) { student.setCode(value); isCode = false; } else if (isAge) { student.setAge(value); isAge = false; } } @Override public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName) throws SAXException { if (qName.equals("student")) { students.add(student); } } }; saxParser.parse("students.xml", defaultHandler); System.out.println(students.toString()); } catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SAXException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |


