By default, MySQL does not allow us to access it from other machines, accessible only from the machine itself. Therefore, if we want to access MySQL from another machine, we must make changes in the configuration of MySQL. What the changes are, in this tutorial, I will guide you.
Note: This tutorial, I wrote for MySQL server installed on the machine Ubuntu 15.04. The other machines are similar, except for the MySQL installation path.
The first thing we need to do is: to change the configuration of MySQL mysqld.cnf configuration file
In the Ubuntu 15.04, when installed, the mysqld.cnf configuration file will be located:
|
1 |
/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf |
To allow access to MySQL from other machines, we need to remove the bind-address and skip-external-locking configurations in this file by commenting out the following two lines:
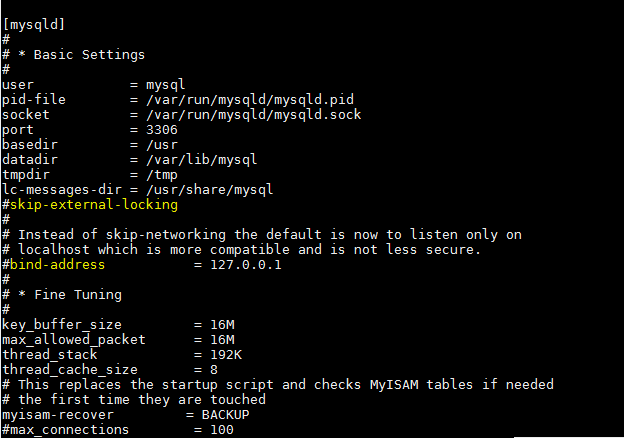
For these changes to take effect, you need to restart your MySQL server.
|
1 |
sudo service mysql restart |
Next, we need to configure it to allow the user to log in from any machine
To allow any user (for example, user root) to login from any machine, we must grant it the following permissions:
– Login to MySQL server
|
1 |
mysql –u root -p |
Enter and then enter the password for the root user.
– Assign all permissions for root user access from another machine
|
1 |
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO root@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; |
– For a change to take effect, we need to run the following command:
|
1 |
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; |
And now you can log into the MySQL server using root user from any machine.


