You already know about Docker and Kubernetes with their benefits in developing, deploying, and running applications on production environments. To make it easy and convenient to use Docker and Kubernetes, a platform called OpenShift has been introduced. OpenShift will make us easy to create Docker Images, easily create Pods containing one or more containers from those Docker images with Kubernetes, easily deploy applications and monitor them. In this tutorial, I will guide you on how to install OpenShift on macOS using Docker and the Command Line Interface oc tool!
To do this, the first thing we need to do is make sure Docker and oc tool are installed on your computer.
One thing to keep in mind is that the latest versions of Docker Desktop for Mac are currently having issues with Proxy support to pull or push Docker Image onto Docker Registry.
During the deployment of an application, OpenShift will need to pull or push Docker Image onto an OpenShift Docker Registry with IP of 172.30.1.1, the latest versions of Docker Desktop for Mac, fix the Docker’s Proxy information when connecting to OpenShift Docker Registry and not giving us by-pass this IP address.
Only version 17.09.1-ce-mac42 is working normally with this function.
So, please download Docker Desktop for Mac version 17.09.1-ce-mac42 at https://download.docker.com/mac/stable/21090/Docker.dmg and install it!
Mine is as follows:
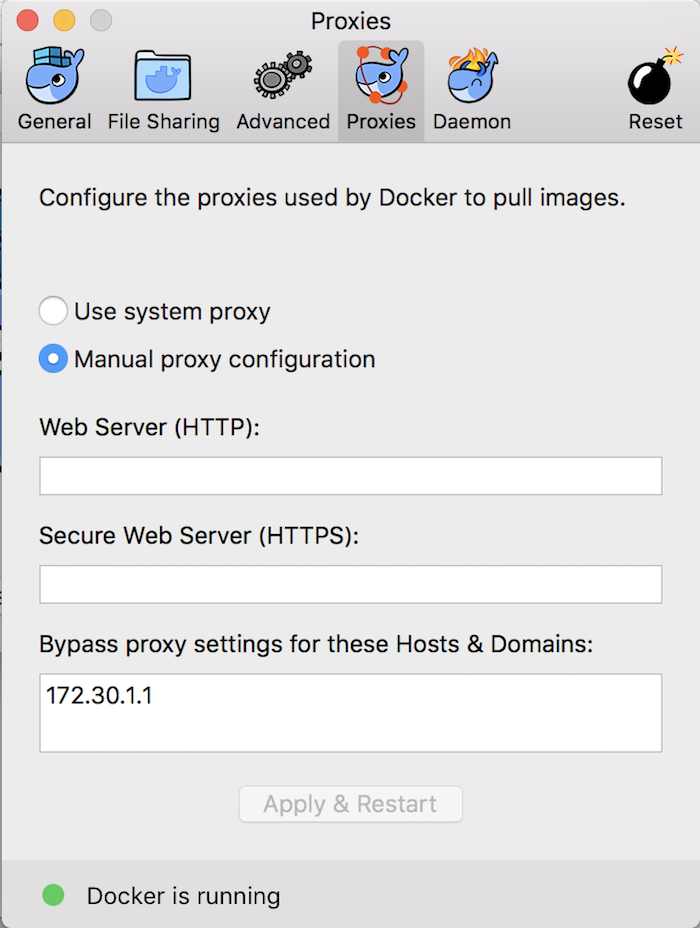
You need to configure the Proxies tab to by-pass IP 172.30.1.1 as follows:
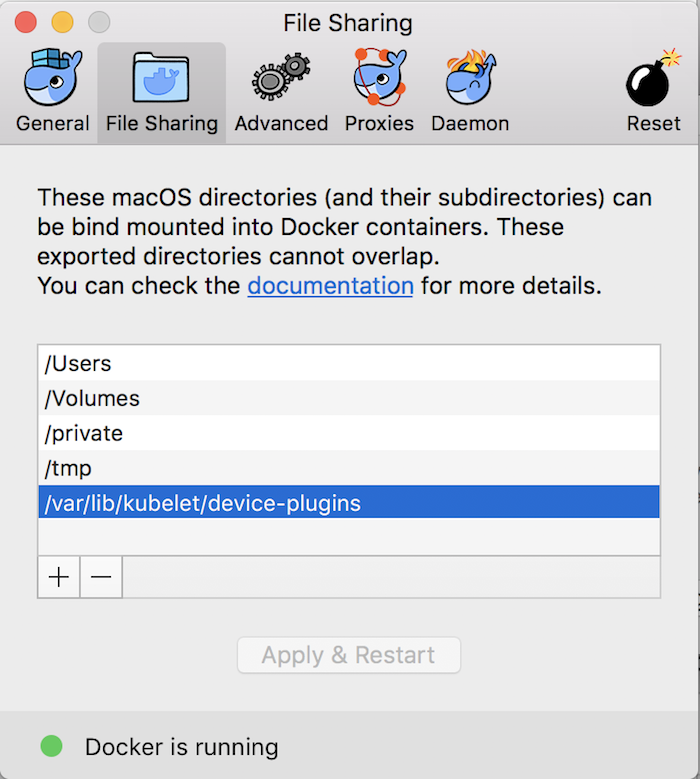
Another thing you need to do to be able to install OpenShift with this version of Docker is to create a folder called device-plugins at /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins and configure it in the File Sharing tab as follows:
Remember to set permissions for this folder:
|
1 |
sudo chmod 777 /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins |
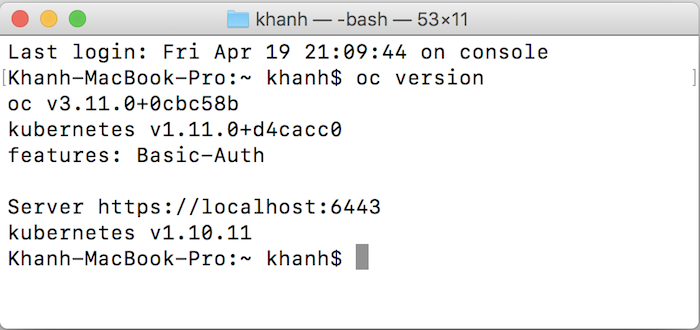
My Command Line Interface oc is as follows:
Next, you need to run the “oc cluster up” command to install OpenShift.
|
1 |
oc cluster up |
When running the above command, you may get the following error on macOS:
|
1 |
error: did not detect an --insecure-registry argument on the Docker daemon |
then, you can add an insecure-registry 172.30.0.0/16 to Docker’s Daemon tab:
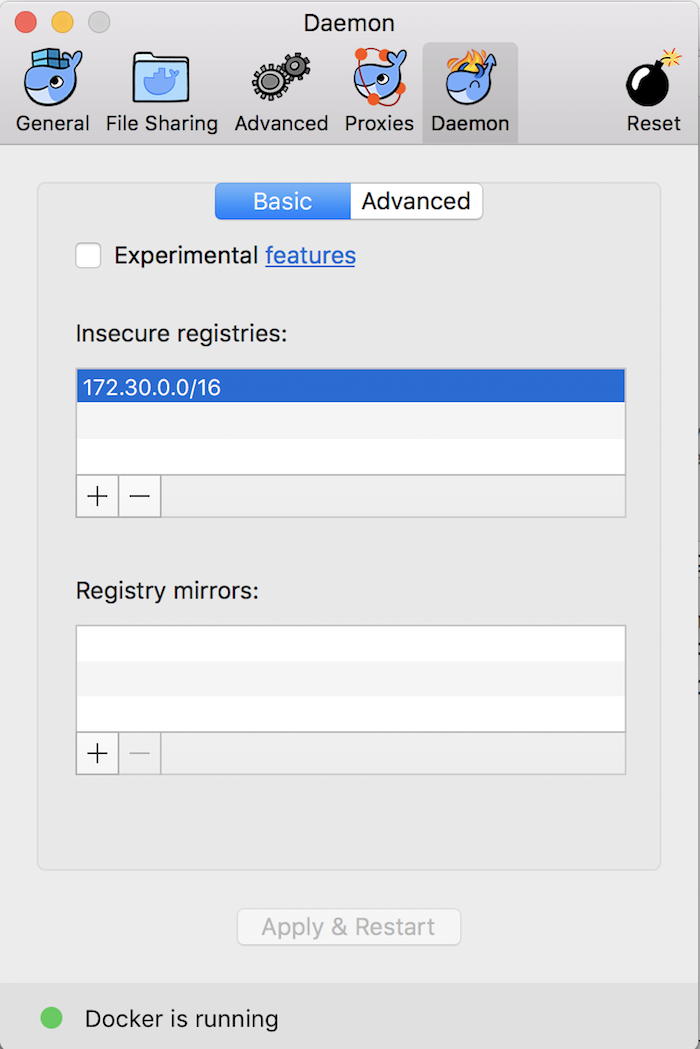
then rerun the above command.
Or you can run the oc cluster up command as follows:
|
1 |
oc cluster up --skip-registry-check=true |
if you do not want to add insecure registry 172.30.0.0/16 on Docker’s Daemon tab.
If the following error occurs:
|
1 2 |
W0419 23:09:37.639104 1572 up.go:696] Port forwarding requires socat command line utility.Cluster public ip may not be reachable. Please make sure socat installed in your operating system. error: exec: "socat": executable file not found in $PATH |
then use macOS Homebrew to install socat:
|
1 |
brew install socat |
Result:
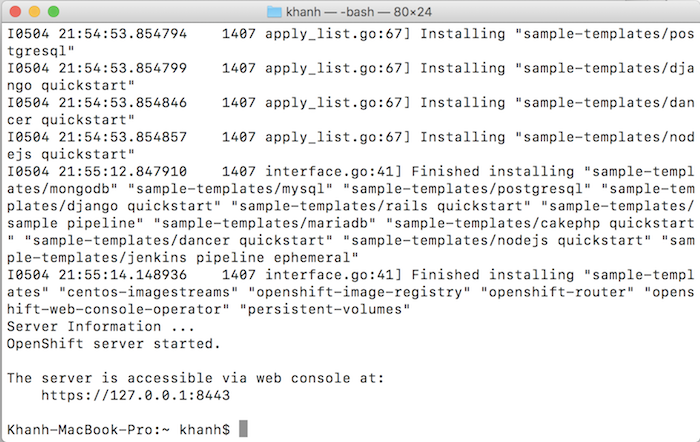
Now you can login to OpenShift using the oc or web console tool!
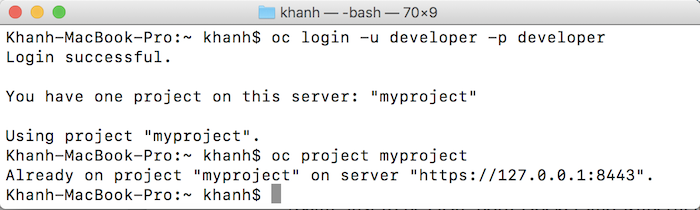
With the oc tool, you can use the following command:
|
1 |
oc login -u developer -p developer |
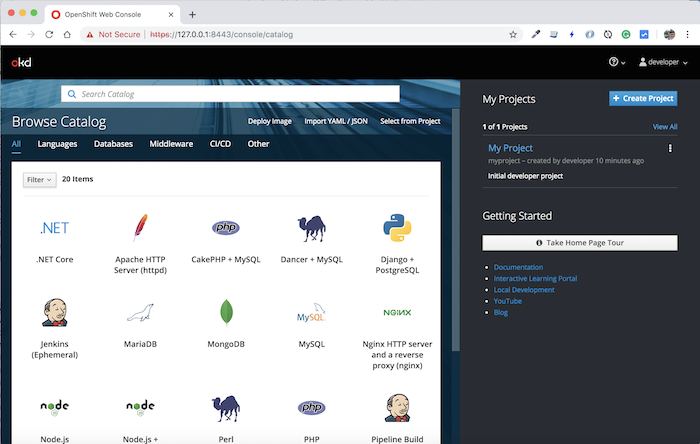
If using the web console, please open the browser and go to the following address: https://127.0.0.1:8443/console/. You will see the login screen as follows:

Using user as developer with password is any character to login, you will see the following result:
Now that we’re done installing OpenShift, guys.


