Trong bài viết trước, mình đã giới thiệu với các bạn về GraphQL, những vấn đề mà GraphQL đã giải quyết được cho những hạn chế của RESTful Web Service. Mình cũng đã hướng dẫn sơ qua cho các bạn về cách hiện thực type Query của GraphQL với Spring GraphQL và Spring Data JPA. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu chi tiết hơn về cách hiện thực type Query này sử dụng Spring GraphQL với Spring Data R2DBC các bạn nhé!
Đầu tiên, mình sẽ tạo một Spring Boot project với Spring Web, Spring for GraphQL, Spring Data R2DBC và PostgreSQL Driver để làm ví dụ:
Kết quả:
Như mình đã nói trong bài viết trước, để làm việc với GraphQL, chúng ta cần định nghĩa các tập tin schema .graphqls. Mặc định thì Spring Boot sẽ scan tất cả các thư mục trong classpath src/main/resources của project để đọc các tập tin schema này.
Mình sẽ tạo một thư mục tên là graphql trong thư mục src/main/resources và để các tập tin schema của GraphQL trong thư mục này.
Để làm ví dụ mình đã tạo mới tập tin schema.graphqls để truy vấn thông tin tất cả sinh viên trong database như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
type Query { students: [Student] } type Student { id: ID, name: String } |
Để handle cho Query trên, đầu tiên, mình sẽ định nghĩa class Repository cho table “student”:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
CREATE TABLE student ( id bigint NOT NULL, name varchar(50) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) |
như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
package com.huongdanjava.graphql; import org.springframework.data.r2dbc.repository.R2dbcRepository; public interface StudentRepository extends R2dbcRepository<Student, Long> { } |
với Student model có nội dung như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
package com.huongdanjava.graphql; import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id; import org.springframework.data.relational.core.mapping.Table; @Table public class Student { @Id private Long id; private String name; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } |
Tiếp theo, chúng ta sẽ tạo mới một controller và định nghĩa một method có tên giống với tên field của type Query trên, như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package com.huongdanjava.graphql; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.QueryMapping; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @Controller public class GraphQLController { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @QueryMapping public Flux<Student> students() { return studentRepository.findAll(); } } |
Như các bạn thấy, phương thức students() đã được annotate với annotation @QueryMapping giúp cho Spring có thể scan và map tên method này với field của type Query. Rất đơn giản phải không các bạn?
Behind the sense, thì annotation @QueryMapping được implement sử dụng một generic annotation là @SchemaMapping:
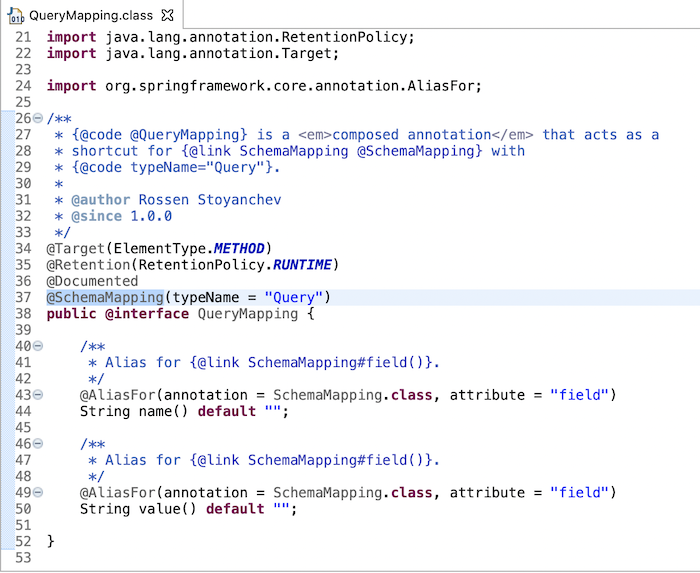
Annotation @SchemaMapping này định nghĩa một thuộc tính là typeName cho phép chúng ta định nghĩa type của GraphQL. Ở đây, type của chúng ta là Query đó các bạn!
Một thuộc tính khác của annotation @SchemaMapping là field, giúp Spring có thể map field của GraphQL với tên method sẽ handle request:
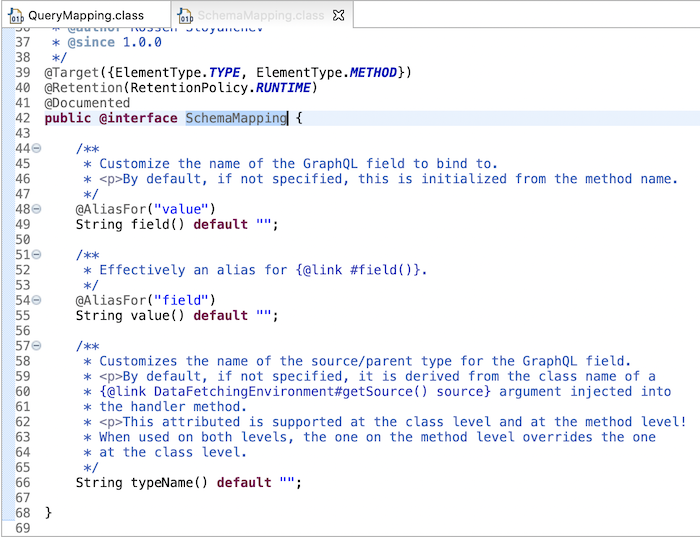
Mặc định nếu chúng ta không khai báo giá trị cho thuộc tính field này, giá trị của nó sẽ là tên method các bạn nhé!
Nếu không sử dụng annotation @QueryMapping, chúng ta có thể viết lại code ở trên sử dụng annotation @SchemaMapping như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package com.huongdanjava.graphql; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.SchemaMapping; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @Controller public class GraphQLController { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @SchemaMapping(typeName = "Query", field = "students") public Flux<Student> getAllStudents() { return studentRepository.findAll(); } } |
Để tiện cho việc testing, chúng ta sẽ thêm property spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=true để enable sử dụng công cụ GraphiQL, trong tập tin application.properties:
|
1 |
spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=true |
Thông tin database cũng được cấu hình trong tập tin application.properties như sau:
|
1 2 3 |
spring.r2dbc.url=r2dbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/student spring.r2dbc.username=khanh spring.r2dbc.password=1 |
Database của mình có những sinh viên như sau:
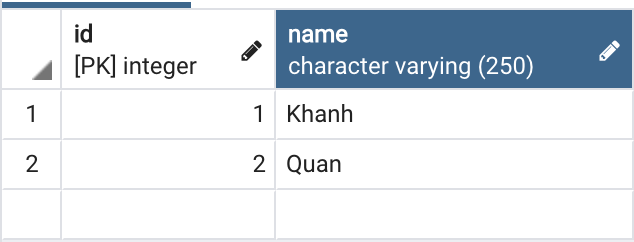
Bây giờ, nếu chạy ứng dụng này và query sử dụng field “students” trên, các bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau:
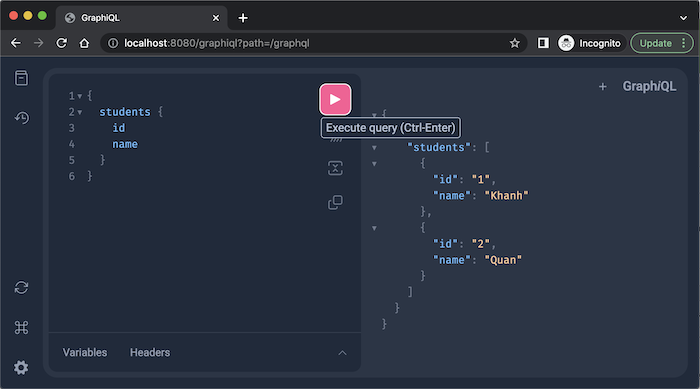
Để truyền tham số cho một Query, chúng ta có thể định nghĩa ví dụ như sau:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
type Query { students: [Student] studentById(id: Int): Student } type Student { id: ID, name: String } |
Trong controller, chúng ta sẽ sử dụng annotation @Argument để bind tham số được định nghĩa trong field của Query với tham số trong method handle request:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com.huongdanjava.graphql; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.Argument; import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.QueryMapping; import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.SchemaMapping; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; @Controller public class GraphQLController { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @SchemaMapping(typeName = "Query", field = "students") public Flux<Student> getAllStudents() { return studentRepository.findAll(); } @QueryMapping public Mono<Student> studentById(@Argument("id") Long id) { return studentRepository.findById(id); } } |
Thuộc tính id của annotation @Argument này cho phép chúng ta chỉ định rõ tham số trong method được bind với tham số nào trong Query.
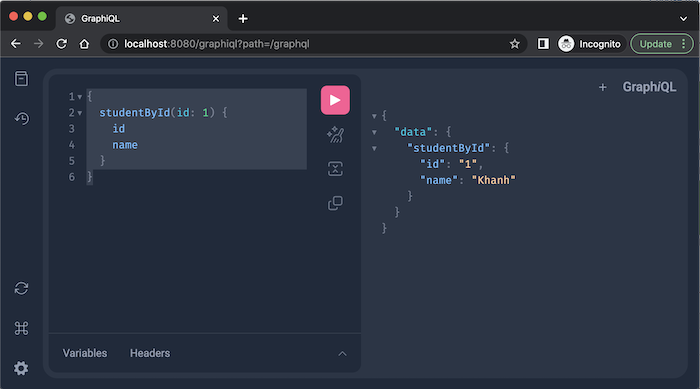
Kết quả khi chúng ta query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ studentById(id: 1) { id name } } |
như sau: